Planning for retirement can feel overwhelming, but choosing the right type of Individual Retirement Account (IRA) is one of the best ways to start building long-term wealth. Two of the most popular options are the Roth IRA and the Traditional IRA. Both accounts offer tax advantages—but in very different ways.
This guide breaks down the key differences between Roth and Traditional IRAs, their pros and cons, and how to choose the best option for your financial goals.
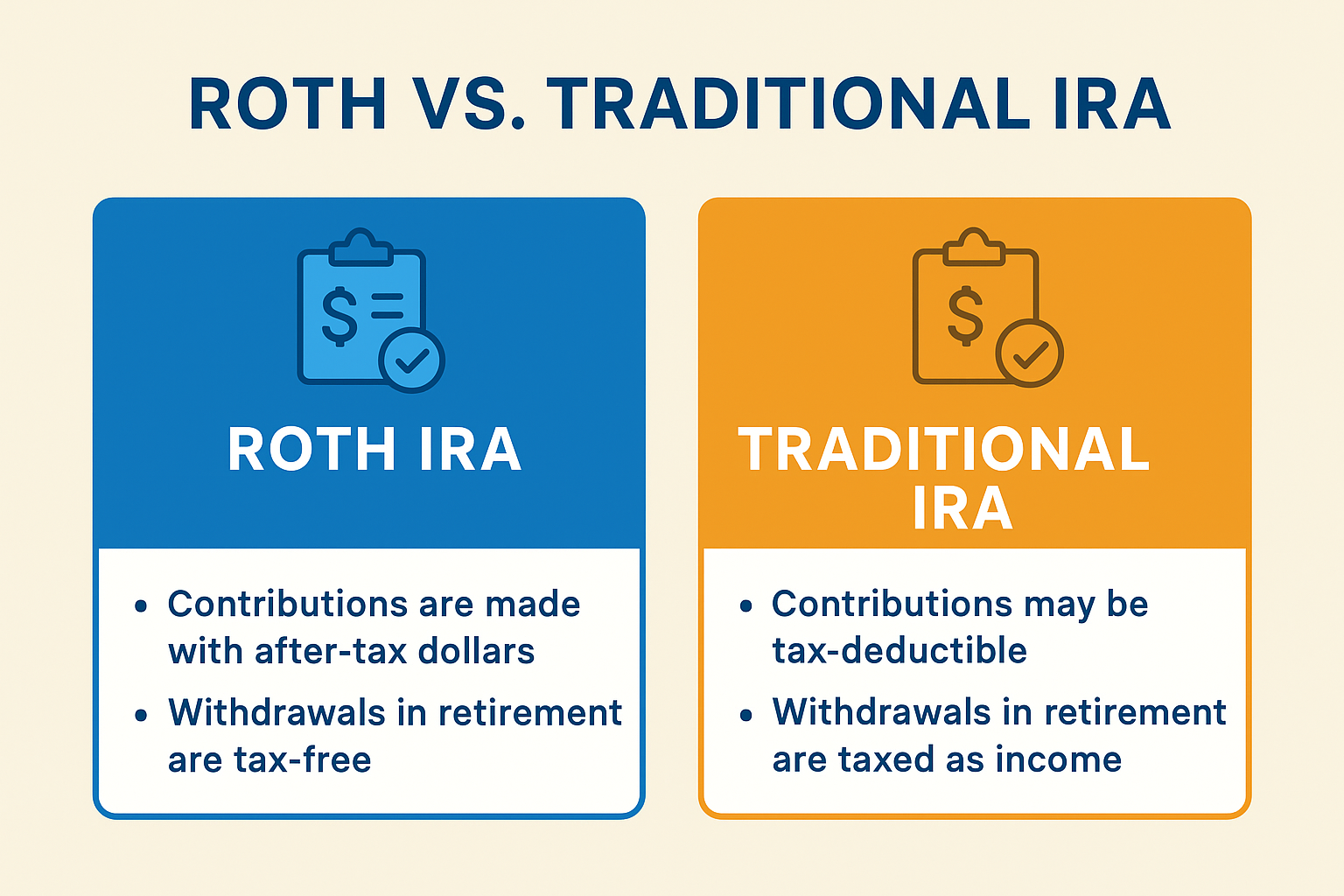
What Is a Roth IRA?
A Roth IRA allows you to contribute money that has already been taxed. The big advantage?
Your withdrawals in retirement are tax-free, as long as you follow IRS rules.
Key features of a Roth IRA:
- Contributions are made with after-tax dollars.
- Qualified withdrawals in retirement are 100% tax-free.
- You can withdraw your contributions (but not earnings) at any time without penalty.
- Income limits apply for eligibility.
Best for: Younger workers or anyone who expects to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement.
What Is a Traditional IRA?
A Traditional IRA allows you to contribute pre-tax dollars, which can lower your taxable income today. However, withdrawals in retirement are taxed as regular income.
Key features of a Traditional IRA:
- Contributions may be tax-deductible (depending on income and workplace retirement plan access).
- Growth is tax-deferred until you withdraw.
- Withdrawals in retirement are taxed as income.
- Required minimum distributions (RMDs) begin at age 73.
Best for: People who want an immediate tax break and expect to be in a lower tax bracket after retiring.
Roth IRA vs. Traditional IRA: Key Differences
| Feature | Roth IRA | Traditional IRA |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Treatment | Pay taxes now, tax-free withdrawals later | Tax deduction now, pay taxes later |
| Income Limits | Yes, based on your Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) | No income limits for contributions |
| Withdrawals | Tax-free in retirement | Taxed as regular income |
| Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs) | None | Start at age 73 |
| Best For | Those expecting higher taxes later | Those wanting an upfront tax break |
Pros and Cons of Each IRA Type
Roth IRA Pros
- Tax-free withdrawals in retirement
- No required minimum distributions
- Flexibility to withdraw contributions at any time
Roth IRA Cons
- No immediate tax deduction
- Income limits may restrict eligibility
Traditional IRA Pros
- Possible immediate tax deduction
- No income limits for contributions
- Good for reducing taxable income now
Traditional IRA Cons
- Withdrawals are taxed as income
- Required minimum distributions start at 73
How to Choose Between a Roth and Traditional IRA
Ask yourself these questions to decide which account works best for you:
- Do I need a tax break now or later?
- Choose a Traditional IRA if you want to lower your taxable income today.
- Choose a Roth IRA if you prefer tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
- What tax bracket will I be in later?
- If you expect higher taxes in retirement, a Roth may save you more.
- Am I eligible for a Roth IRA?
- Check current income limits set by the IRS.
Final Thoughts
Both Roth and Traditional IRAs are powerful tools for building retirement savings. The right choice depends on your income, tax situation, and long-term goals. For many people, a combination of both accounts—if eligible—provides the best balance of tax advantages now and in the future.